Differentiated instruction involves tailoring teaching methods to meet diverse student needs, ensuring inclusive environments․ It balances academic content with individual learning requirements for effective education․
1․1․ Definition and Importance of Differentiated Instruction
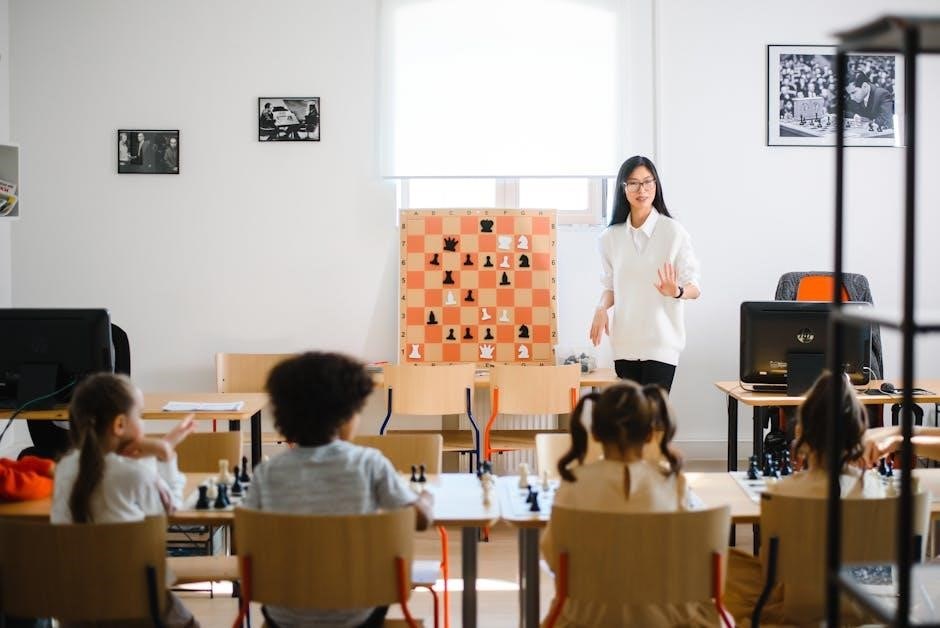
Differentiated instruction is a teaching approach that tailors methods, resources, and assessments to meet diverse student needs, ensuring inclusivity․ It balances academic content with individual learning requirements, fostering engagement and equity․ This strategy acknowledges variations in abilities, learning styles, and interests, creating personalized pathways for success․ By addressing these differences, differentiated instruction promotes higher academic performance and fosters a supportive classroom environment․ Its importance lies in its ability to cater to all learners, ensuring no student is left behind․ This approach is vital for creating inclusive classrooms where every student feels valued and empowered to achieve their full potential․
1․2․ The Role of Differentiated Instruction in Inclusive Classrooms
Differentiated instruction plays a pivotal role in creating inclusive classrooms by addressing the diverse needs of all students․ It ensures that each learner, regardless of their abilities, interests, or backgrounds, has access to meaningful learning opportunities․ By modifying curriculum content, teaching methods, and assessments, educators can cater to individual differences, fostering a culture of equity and accessibility․ This approach not only supports academic growth but also promotes social inclusion, helping students feel valued and respected․ In inclusive classrooms, differentiated instruction serves as a cornerstone, enabling teachers to maximize learning potential and create environments where every student can thrive and succeed․
Key Principles of Inclusive Classrooms
Inclusive classrooms are built on equity, accessibility, and respect for diversity․ They foster a supportive environment where all students can engage, grow, and succeed together meaningfully․
2․1․ Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework that ensures learning environments are flexible and accessible to all students․ It emphasizes engagement, representation, and action and expression, providing multiple ways for students to access content, demonstrate knowledge, and stay motivated․ By incorporating UDL principles, educators create inclusive classrooms where diverse learners can thrive․ This approach minimizes barriers and maximizes opportunities for participation, aligning with differentiated instruction strategies․ UDL’s focus on flexibility and accessibility ensures that every student can engage meaningfully with curriculum, fostering an inclusive and equitable learning environment tailored to individual needs and preferences․
2․2․ The Importance of Ongoing Assessment
Ongoing assessment is a cornerstone of effective differentiated instruction in inclusive classrooms․ It involves continuously monitoring student progress to understand their strengths, challenges, and learning needs․ By gathering data through formative assessments, quizzes, and observations, teachers can make informed decisions about instruction․ This process helps identify gaps in understanding and ensures that all students receive targeted support․ Regular assessment also allows for timely adjustments to teaching strategies, ensuring that instruction remains relevant and engaging․ Ultimately, ongoing assessment fosters a growth mindset, enabling teachers to meet diverse needs and promote equitable learning opportunities for all students in an inclusive environment․

Specific Strategies for Differentiated Instruction
Specific strategies include tiered activities, flexible grouping, learning menus, scaffolding, and formative assessments․ These approaches ensure personalized learning experiences for all students in inclusive classrooms․
3․1․ Tiered Activities
Tiered activities are a cornerstone of differentiated instruction, allowing teachers to cater to varying student skills and readiness levels․ By designing tasks at foundational, intermediate, and advanced levels, educators ensure each student engages meaningfully․ This strategy promotes inclusivity by addressing diverse learning needs․ For instance, foundational tiers focus on core concepts, while advanced tiers offer challenges for high-achievers․ Tiered activities ensure that all students are appropriately challenged, fostering growth and engagement․ This approach is particularly effective in inclusive classrooms, where diverse learners benefit from structured yet flexible learning pathways that align with their individual capabilities and interests․
3․2․ Flexible Grouping
Flexible grouping is a dynamic strategy that organizes students into temporary or permanent groups based on specific criteria like skill level, interest, or learning needs․ This approach allows teachers to tailor instruction to meet diverse student requirements, fostering an inclusive classroom environment․ By regrouping students as needed, educators can address varied learning styles and ensure each student receives appropriate challenges and support․ Flexible grouping enhances collaboration, as students work with peers who share similar goals or interests․ This method promotes equity, engagement, and personalized learning, making it a powerful tool for managing diverse classrooms and ensuring all students have opportunities to succeed․
3․3․ Learning Menus and Choice Boards
Learning menus and choice boards are innovative tools that empower students to take ownership of their learning․ These strategies provide structured options for students to select activities that align with their learning style, readiness, and interests․ Menus often include tiered tasks, while choice boards present visual, organized selections․ Both methods allow for personalized learning experiences, fostering engagement and motivation․ By offering choices, teachers cater to diverse needs and promote autonomy․ This approach ensures that students are challenged appropriately and can work at their own pace, making it an effective way to differentiate instruction in inclusive classrooms and enhance academic performance․ Choice boards also encourage creativity and critical thinking․
3․4․ Scaffolding Techniques
Scaffolding techniques provide temporary support to students as they learn new concepts, helping bridge gaps between their current understanding and desired learning outcomes․ This strategy involves breaking tasks into manageable steps, using visual aids, and offering guided practice․ Teachers gradually release responsibility to students as they gain confidence and independence․ Scaffolding is particularly effective in inclusive classrooms, where learners may have varying abilities and needs․ By adapting instruction to meet individual levels, teachers ensure equitable access to learning․ This approach fosters a supportive environment, encouraging students to take risks and build upon their strengths while addressing challenges․ Scaffolding is essential for promoting personalized and meaningful learning experiences․
3․5․ Formative Assessments
Formative assessments are ongoing evaluation tools used to monitor student progress and understanding during the learning process․ These assessments provide immediate feedback to both teachers and students, allowing for timely adjustments to instruction․ Through methods like exit tickets, quizzes, and class discussions, teachers can identify knowledge gaps and adjust lessons to meet individual needs․ Formative assessments are crucial in inclusive classrooms as they help ensure all students are on track to meet learning goals․ By regularly checking in with students, teachers can differentiate instruction more effectively, ensuring no learner is left behind․ This approach fosters a responsive and adaptive teaching environment, promoting equity and student success․

Technology Integration
Technology integration enhances differentiated instruction by providing diverse learning tools and resources․ It supports personalized learning, increases engagement, and ensures accessibility for all students, fostering inclusivity․
4․1․ Assistive Technology Tools
Assistive technology tools are essential for creating inclusive classrooms, enabling students with disabilities to access learning materials effectively․ These tools, such as text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and audio descriptions, provide equal opportunities for all learners․ They help bridge gaps in accessibility, ensuring diverse needs are met․ By integrating these technologies, educators can cater to various learning styles and abilities, fostering an inclusive environment․ Assistive technologies not only support students with disabilities but also enhance overall classroom engagement and participation, making education more equitable and accessible for everyone․ Their implementation is a cornerstone of differentiated instruction in modern, inclusive educational settings․
4․2․ Educational Software for Differentiated Instruction
Educational software plays a pivotal role in differentiated instruction by providing tailored learning experiences for diverse student needs․ Tools like learning management systems (LMS) and adaptive learning platforms allow teachers to customize content, pace, and delivery․ Multimedia resources, such as interactive simulations and virtual labs, engage students with varying learning styles․ Software like Khan Academy and Duolingo offers personalized lessons, while tools like Google Classroom facilitate flexible grouping․ These technologies enable real-time progress tracking, allowing educators to adjust instruction dynamically․ By integrating educational software, teachers can create a more inclusive and engaging learning environment, ensuring all students have opportunities to succeed and grow academically․

Culturally Responsive Teaching
Culturally responsive teaching fosters inclusivity by incorporating diverse perspectives and student backgrounds into instruction, promoting equity and engagement for all learners in inclusive classrooms․
5․1․ Incorporating Diverse Perspectives
Incorporating diverse perspectives into teaching ensures cultural responsiveness, fostering an inclusive classroom environment․ By integrating multicultural resources and student-centered practices, educators acknowledge and value learners’ unique backgrounds․ This approach promotes equity and engagement, as students see their experiences reflected in the curriculum․
Using diverse texts, images, and examples helps break down stereotypes and broadens students’ understanding of global cultures․ Additionally, encouraging student voice and participation creates a safe space for sharing perspectives, enhancing social-emotional learning and collaboration․
Such strategies not only enrich the learning experience but also empower students to connect with the material on a personal level, making education more meaningful and accessible for all learners in inclusive classrooms․

Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) fosters self-awareness, empathy, and relationship skills, creating a supportive environment․ It promotes inclusivity by addressing emotional needs, ensuring all students feel valued and connected in the classroom․
6․1․ Promoting Inclusivity Through SEL
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) plays a pivotal role in fostering inclusivity by equipping students with essential life skills such as self-awareness, empathy, and relationship-building․ SEL encourages students to understand and respect diverse perspectives, creating a culture of belonging․ By addressing emotional and social needs, SEL helps students navigate interpersonal challenges, reducing conflicts and fostering cooperation․ In inclusive classrooms, SEL strategies ensure that all students, regardless of their background or abilities, feel valued and supported․ This approach not only enhances academic performance but also cultivates a positive classroom environment where diversity is celebrated and every student thrives emotionally and socially․
Parental Involvement
Collaborating with families enhances differentiated instruction by fostering communication and shared goals․ Parents’ involvement supports students’ unique needs, creating a cohesive learning environment at home and school․
7․1․ Collaborating with Families
Collaborating with families is essential for creating a cohesive learning environment․ By involving parents in differentiated instruction, teachers can gain insights into students’ strengths and challenges, fostering tailored support․ Regular communication through meetings, updates, and feedback ensures alignment between home and school strategies․ Families can reinforce learning by incorporating personalized techniques at home, enhancing academic outcomes․ Volunteer opportunities and parent-teacher partnerships further strengthen this collaboration, ensuring students receive consistent guidance․ This mutual support system empowers families to actively contribute to their child’s education, creating a unified approach that addresses individual needs and promotes inclusive learning experiences for all students․

Professional Development
Professional development is crucial for educators to master differentiated instruction techniques․ Training programs provide practical strategies and resources to create inclusive classrooms, enhancing teaching effectiveness and student outcomes․
8․1․ Training for Effective Differentiated Instruction
Training for differentiated instruction equips educators with practical strategies to meet diverse student needs․ Workshops and professional development programs focus on tailored teaching methods, fostering inclusive classrooms․ These sessions often include modeling techniques, collaborative planning, and hands-on activities to enhance instructional design․ Educators learn to integrate Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles, tiered activities, and formative assessments to create engaging, student-centered learning environments․ Effective training emphasizes real-world application, ensuring teachers can implement differentiated strategies seamlessly․ This professional growth not only enhances teaching effectiveness but also promotes equity and accessibility, benefiting all learners and fostering a culture of inclusivity and academic success․





