Shoulder dislocation is a common injury affecting daily activities and sports. Rehabilitation exercises are crucial for restoring mobility‚ strength‚ and stability‚ preventing future dislocations and enhancing recovery.
1.1 Understanding Shoulder Dislocation and Its Impact
Shoulder dislocation occurs when the humerus detaches from the glenoid‚ often due to trauma. Anterior dislocations are the most common‚ severely impacting joint stability and mobility. This injury can disrupt daily activities and sports‚ causing pain and weakness. Understanding its mechanisms and types is crucial for effective rehabilitation and preventing recurrent episodes‚ emphasizing the need for targeted exercises to restore function and strength.
1.2 The Role of Exercise Therapy in Recovery
Exercise therapy is vital for shoulder dislocation recovery‚ enhancing strength‚ stability‚ and mobility. It reduces pain and recurrence risk‚ restoring function for daily activities and sports. Tailored programs‚ including isometric and plyometric exercises‚ promote gradual progression and long-term health‚ ensuring effective rehabilitation and preventing future injuries through consistent practice and adherence to prescribed routines.
Immediate Post-Injury Care and Initial Exercises
Post-injury care involves immobilization with a sling and pain management. Gentle exercises begin early to maintain mobility‚ reduce stiffness‚ and promote healing without causing further damage.
2.1 Immobilization and Pain Management
Immobilization using a supportive sling is crucial to protect the shoulder post-injury‚ reducing movement and pain. Pain management often includes ice therapy‚ medication‚ or physical methods to alleviate discomfort. Proper rest and immobilization help prevent further injury‚ allowing tissues to begin healing. This phase is vital for setting the foundation for successful rehabilitation and early recovery from shoulder dislocation.
2.2 Gentle Range-of-Motion Exercises for the Shoulder
Gentle range-of-motion exercises are introduced early to maintain shoulder mobility without causing further injury. These include pendulum swings‚ shoulder circles‚ and passive movements. They help reduce stiffness‚ improve circulation‚ and promote healing. Done 2-3 times daily‚ these exercises are essential for restoring flexibility and preparing the shoulder for more intensive rehabilitation‚ minimizing the risk of long-term limitations in movement and strength.

Phase-Based Rehabilitation Programs
Phase-based rehab programs offer a structured‚ progressive approach to recovery‚ addressing pain‚ mobility‚ strength‚ and function across acute‚ subacute‚ and advanced stages for optimal outcomes.
3.1 Acute Phase (0-2 Weeks): Pain Reduction and Basic Mobility
The acute phase focuses on reducing pain and inflammation while restoring basic shoulder mobility. Immobilization with a sling is often recommended to protect the joint. Gentle exercises‚ such as shoulder circles and pendulum swings‚ are introduced to prevent stiffness. Pain management strategies‚ including ice therapy‚ are emphasized. Early physical therapy guidance ensures a safe transition to more active movements‚ laying the foundation for recovery.
3.2 Subacute Phase (2-6 Weeks): Strengthening and Stability
The subacute phase emphasizes strengthening the shoulder muscles‚ particularly the rotator cuff‚ through controlled exercises. Isometric exercises‚ such as shoulder holds‚ and resistance bands are commonly used to improve stability. Gradual progression to dynamic movements‚ like arm raises and external rotations‚ helps restore functional strength. These exercises are tailored to individual progress‚ ensuring the shoulder joint becomes more resilient to future dislocations while maintaining proper alignment and movement patterns.
3.3 Advanced Phase (6-12 Weeks): Functional Restoration and Sports-Specific Training
The advanced phase focuses on restoring full shoulder function and preparing for sports or high-demand activities. Exercises include dynamic stabilization drills‚ plyometric movements‚ and sport-specific training to enhance power and control. Activities like overhead throws or dynamic rotations are introduced to mimic real-life movements. Customized programs ensure a smooth transition to normal activities‚ reducing the risk of re-injury while optimizing long-term shoulder performance and resilience.

Isometric and Plyometric Exercises for Shoulder Stability
Isometric exercises build shoulder strength without movement‚ while plyometric exercises enhance dynamic stabilization; Both are essential for restoring stability and preventing recurrent dislocations after shoulder injuries.

4.1 Isometric Exercises to Improve Shoulder Strength
Isometric exercises are essential for rebuilding shoulder strength after dislocation. These exercises‚ such as shoulder holds and wall slides‚ involve contracting muscles without joint movement. They improve stability by activating key muscles like the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers. Performing 3 sets of 10 repetitions daily can enhance strength and reduce the risk of future dislocations. Progress to dynamic exercises once baseline strength is achieved.
4.2 Plyometric Exercises for Dynamic Stabilization
Plyometric exercises‚ such as medicine ball throws and plyometric pushes‚ enhance dynamic shoulder stabilization. These high-intensity movements improve neuromuscular control and joint stability‚ reducing dislocation risk. Start with low-intensity drills‚ focusing on proper form to avoid injury. Progress to more dynamic movements as strength and confidence grow. Incorporate 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions for optimal results. These exercises are particularly beneficial for athletes returning to sports after shoulder dislocation.
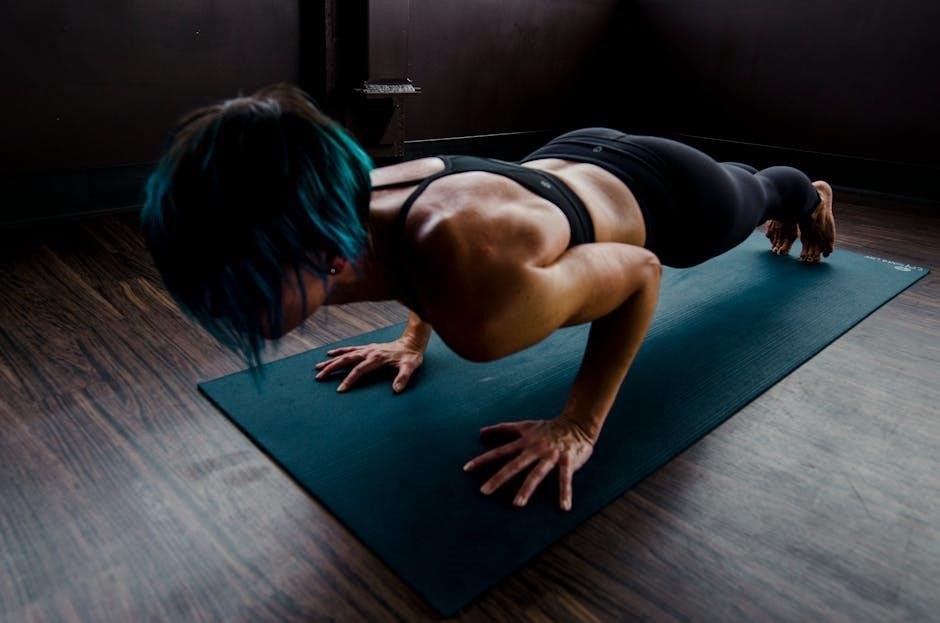

Scapular-Focused Exercises for Long-Term Stability
Scapular-focused exercises‚ such as scapular push-ups and shoulder blade squeezes‚ improve posture and reduce dislocation risk. They strengthen muscles around the shoulder‚ enhancing long-term stability and preventing recurrence.
5.1 Scapular Stabilization Techniques
Scapular stabilization techniques focus on strengthening muscles like the serratus anterior and trapezius to improve shoulder blade positioning. Exercises such as scapular push-ups and shoulder blade squeezes enhance stability‚ reducing dislocation risk. Proper technique ensures activation of key muscles‚ promoting optimal shoulder mechanics. These techniques are essential for long-term stability‚ preventing recurrent dislocations and enhancing athletic performance. Regular practice helps maintain proper posture and reduces shoulder strain during daily activities.
5.2 Integrating Scapular Exercises into Daily Routines
Incorporating scapular exercises into daily routines enhances long-term stability and prevents strain. Simple exercises like wall slides or scapular squeezes can be done during activities such as brushing teeth or sitting at a desk. Consistency is key to maintaining proper posture and reducing the risk of dislocation. These exercises promote muscle memory‚ ensuring the shoulders remain stable even during dynamic movements‚ fostering overall shoulder health and resilience.
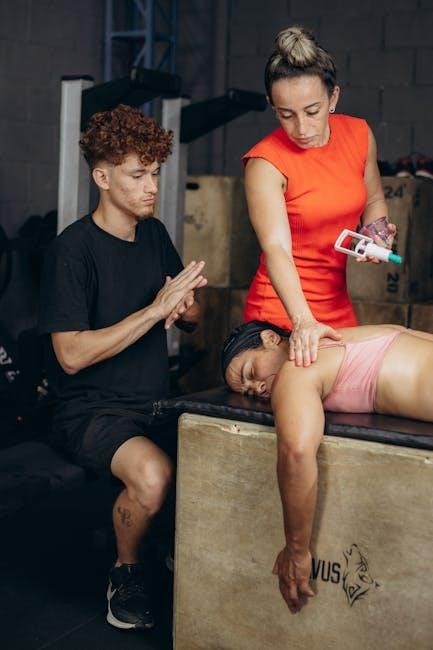

Physical Therapy and Customized Exercise Plans
Physical therapy is essential for recovery‚ with a therapist creating personalized exercise plans to enhance strength‚ mobility‚ and stability‚ tailored to each patient’s progress and goals.
6.1 The Role of a Physical Therapist in Rehabilitation
A physical therapist plays a vital role in rehabilitation by designing personalized exercise programs‚ conducting regular assessments‚ and using techniques like manual therapy and ice/heat to aid recovery. They ensure exercises are performed correctly‚ monitor progress‚ and adjust plans to meet individual needs‚ promoting optimal healing and restoring function. Their expertise is key to effective rehabilitation from shoulder dislocation.
6.2 Tailoring Exercises to Individual Needs and Progress
Exercises must be tailored to each patient’s specific needs‚ injury severity‚ and progress. This involves modifying intensity‚ duration‚ and complexity based on individual recovery stages. A phased approach ensures gradual progression from basic range-of-motion to strengthening and dynamic stabilization exercises. Regular assessments allow adjustments to maintain effectiveness and safety‚ ensuring optimal recovery and minimizing recurrence risk. Customization is key to achieving long-term shoulder stability and function.
Preventing Recurrent Dislocations Through Exercise
Consistent exercise strengthens shoulder muscles‚ improving stability and reducing dislocation risk. Targeted routines focus on rotator cuff and scapular strength‚ promoting long-term joint health and functionality.
7.1 Strengthening the Rotator Cuff and Surrounding Muscles
Strengthening the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles is essential for preventing recurrent shoulder dislocations. Exercises like external rotations‚ internal rotations‚ and scapular stabilizations target these areas‚ enhancing joint stability. Progressing from isometric to dynamic exercises improves muscle endurance and strength. Consistency in these routines helps restore normal shoulder mechanics‚ reducing the risk of future injuries and promoting long-term shoulder health.
7.2 Maintenance Programs for Long-Term Shoulder Health
Maintenance programs are vital for sustained shoulder health after recovery. These include regular exercises targeting the rotator cuff and scapular muscles‚ promoting stability and strength. Incorporating activities like yoga or swimming can enhance flexibility and endurance. Consistent adherence to these routines reduces the risk of recurrence and supports overall joint functionality‚ ensuring long-term stability and mobility in the shoulder joint.

Consistent rehabilitation exercises are essential for recovery and preventing recurrent dislocations. Proper guidance and adherence to tailored programs ensure long-term shoulder stability and functional restoration‚ promoting optimal health.
8.1 Summary of Key Rehabilitation Principles
A structured rehabilitation approach is essential for recovery‚ emphasizing consistency and gradual progression. Early immobilization and pain management are followed by gentle exercises to restore mobility. Strengthening and stability exercises‚ including isometrics and plyometrics‚ are introduced to enhance shoulder function. Scapular stabilization and functional training are critical for long-term stability. Tailored programs and physical therapy guidance ensure personalized recovery‚ promoting optimal outcomes and reducing recurrence risks.
8.2 Encouraging Lifelong Shoulder Care and Exercise
Consistent exercise and proper shoulder care are vital for long-term health. Regular routines prevent future injuries and maintain stability. Incorporate strength and mobility exercises into daily life‚ focusing on posture and scapular health. Educate patients on the importance of adherence and gradual progression. Encourage seeking professional guidance for personalized plans and support. Lifelong care ensures sustained function and reduces recurrence risks‚ promoting active lifestyles and overall well-being.

Additional Resources and Downloads
Downloadable PDF guides provide comprehensive shoulder dislocation exercise routines. Access detailed rehabilitation protocols‚ exercise sheets‚ and recovery tips online through recommended websites and medical publications for further guidance.
9.1 Accessing Shoulder Dislocation Exercise Guides in PDF Format
Comprehensive shoulder dislocation exercise guides in PDF format are widely available online. These guides offer detailed routines‚ including step-by-step instructions and images‚ to aid recovery. They cover exercises for mobility‚ strength‚ and stability‚ catering to various phases of rehabilitation. Many medical websites‚ orthopedic portals‚ and professional physiotherapy platforms provide free or purchasable downloads. Printing these guides allows for easy reference during daily workouts‚ ensuring consistency in the rehabilitation process.
9.2 Recommended Websites and Publications for Further Reading
For further insights‚ explore reputable websites like orthopedic portals and professional physiotherapy platforms. Publications by experts such as SK Rakhimov and YN Proshchenko provide detailed research on shoulder dislocation management. Additionally‚ medical journals and rehabilitation guides offer evidence-based exercise routines and recovery strategies. These resources are invaluable for understanding advanced techniques and staying updated on the latest rehabilitation practices for shoulder dislocation recovery and prevention.






